
Remember the following mnemonic to state the functions of the kidneys.
"A WET BED"
A: Acid base balance.
W: Water removal.
E: Erythropoesis.
T: Toxin removal.
B: Blood pressure control.
E: Electrolyte balance.
D: Vitamin D activation.

Remember the following mnemonic to state the functions of the kidneys.
"A WET BED"
A: Acid base balance.
W: Water removal.
E: Erythropoesis.
T: Toxin removal.
B: Blood pressure control.
E: Electrolyte balance.
D: Vitamin D activation.

Water soluble vitamins: Vitamin B and C.
Fat soluble vitamins: Vitamins A, D, E, and K.
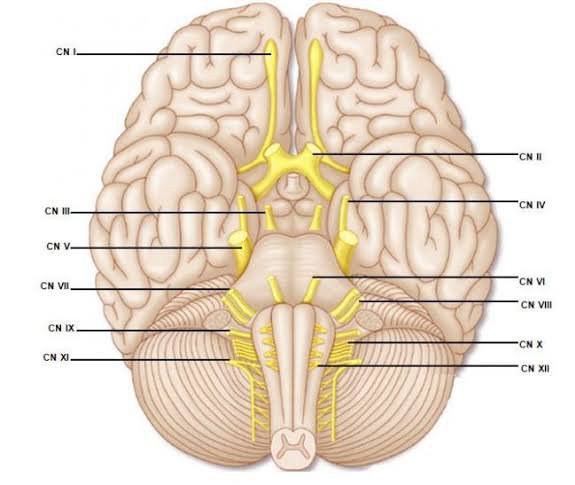
There are totally 12 cranial nerves. They are denoted in Roman numbers from I to XII. These are very easy to remember by just remembering a mnemonic.
Ooh, Ooh, Ooh, To Touch And Feel Very Good Velvet- Such Heaven!
These cranial nerves have different functions. They are mainly divided into sensory, motor, and both. By using the following mnemonic, the function of each cranial nerve can be remembered.
Some Say My Mother Bought My Brother Some Bad Beer, My, My.
Here S stands for sensory, M is for motor, and B is for both.
